User Tools
This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Glossary
Process Planning
A schedule in project management is the chronological and logical arrangement of the work packages of a project. The result of this process planning is the network and is visualized with the help of the Gantt chart. In Projectile, project sequences are defined in the document jump order and realized in the project evaluation.
Offer
An offer contains at least the description of the services to be provided (service specifications, performance specifications) and the calculation of the price to be paid by the client for these services. When submitting a binding offer, the Provider undertakes to carry out the order if the offer is accepted by the Customer. In the case of binding offers, details of payment and delivery conditions and the offer binding period are required.
Relationship
A relationship denotes the quantifiable dependency between events or activities (for example, between two work packages of a project or between two subprojects - see also DIN 69900-1). These relations are defined in Projectile for the visualization of scheduling in the document jump order. In practice, the following relationships are often used:
- Normal Sequence (End - Start)
- Start Sequence (Start - Start)
- End Sequence (End - End)
- Jump Sequence (Start - End)
Work Package
A work package is exactly the activity that a staff member performs for a project in a certain time. A work package is that part of a project which is not further subdivided in the WBS and can be on any level of structure (see also DIN 69901). To achieve the Project goal, it is necessary to process all work packages. In Projectile the work packages are defined in the document type work package. Project times can only be posted in the system to work packages and not to projects.
Client (= Costumer)
A client is the person responsible for a project. The principal approves the project budget and the framework dates. In Projectile the clients are managed in the document type contact. The person responsible for the project is in the role of the contractor vis-à-vis the client of the project. In project management, contract management and procurement deals with the relationship between the roles of the ordering party and the contractor.
Contractor
In commercial terms, the contractor is the seller of a product or service. He is the contractual partner of the client (= customer) who purchases the service agreed in the order.
Effort
The effort of a work package describes (colloquially) the amount of work necessary to produce a defined work result. Unit: person days (PT), person hours (PH).
Estimate of Effort
An estimate of effort is the estimate of the effort required to process a work package. It is based on the experience of the project employee and is the basis for capacity and scheduling. In Projectile you can estimate the target times (i.e. the effort) at project and work package level.
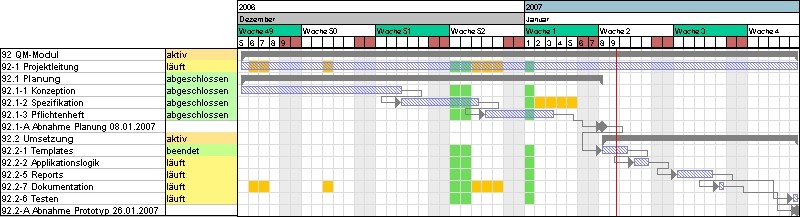
Gantt Chart Network (= Networked Gantt Chart, Network Gantt)
A Gantt chart is an extension of the Gantt chart for displaying the dependencies between work packages relationships and visualized in project evaluation.
Gantt chart (= Gantt diagram) A Gantt chart is a diagram to visualize the time schedule of a project. The duration of a workvpackage or project is symbolized by the length of the bar in the time axis. The bars can include both actual and target data. Events or milestones are represented as points in time. In Projectile, processes are visualized in project evaluation.
Basic Plan
The basic plan comprises all data of an approved project plan on a certain key date (usually release or order placement). The baseline plan contains at least dates, durations, efforts and costs.
Budget, Project Budget
According to DIN 69903, the financial resources made available in a project are the project budget. From an enterprise's point of view, the project budget includes all expenses (that is, personnel costs, travel expenses, external services, material costs, depreciation, and so on) or (from the project manager's point of view) only the funds available to the project manager for project-specific procurements. In Projectile any number budgets.
ButtomUp Planning
ButtomUp planning means project planning according to the ButtomUp principle. In Projectile the ButtomUp planning is used by default. Here the activities, processes, times and costs are not planned in detail at project level, but are started from the work packages. After the rough project planning (definition of upper and lower project without exact time and cost planning) the work packages are defined concretely. By selecting the project, employee, activity and duration, the internal and external costs and duration are determined (see also pricing). These values are assigned to the assigned projects and are passed on to the next project level. All internal and external costs of a sub-project are passed up to the respective top project until the top project (root of the project tree) is reached.
ButtomUp Principle
In project management, the buttom-up principle is the general procedure for processing or planning from work packages to the top project (i.e. from bottom to top: work package - subprojects - top project). An alternative to the ButtomUp principle is the TopDown principle.
Controlling
Controlling is a management subsystem within the company, whose core function is the acquisition, processing and analysis of data in preparation for target-oriented decisions. Project controlling is in turn a subsystem of controlling, which is limited to one or more projects.
CPI
The CPI (Cost Performance Index) is the cost-related performance indicator of Earned Value Analysis. It is formed from the ratio of earned value and actual expenses. This means that if the CPI is greater than 100% (or 1.00), the project results were achieved at lower cost than originally planned, whereas if the CPI is less than 100% (or 1.00), the project is over budget.
Earned Value Analysis
Earned value analysis is a method of making the progress of a project measurable and predictable at any time. The key figure used to do this according to this method is also referred to as earned value. From the three basic variables of earned value, planned and actual expenses, the cost variance, the schedule variance as absolute variables and the cost performance index (CPI) and the schedule performance index (SPI) as relative variables are determined.
Resource Planning (= Capacity Planning)
Resource planning is the planning of the temporal deployment of the resources involved in the project execution, depending on their availability.In Projectile, the planning components consist of the calculation of the free capacities of the individual employees, as well as the planning of the resources.
Degree of Completion
The degree of completion of a work package or project corresponds exactly to the percentage at which the work on a work package or project has been completed. Quantitatively, the POC is the quotient of the actual time and the target time. Qualitatively, it is the percentage at which the project or work package has been completed in terms of content. The status of a project can be determined by the difference between these ratios. In Projectile, qualitative degrees of completion for projects can be defined in the document type degree of completion. The project status and degrees of completion are documented in the project documentation and in the automatically generated status reports.
Progress Report (= Status Reports)
Status reports are an important part of project management and project controlling. They document the progress of the individual subtasks in the project plan. It is clearly visible who is working on what, how far the task has progressed, or what problems or obstacles may exist. Furthermore, due dates are shown and the next upcoming tasks are included. Status reports are distributed to the project manager and all project participants, and form the basis of the status meetings.
Release
Depending on the context, release means the approval of a project, the release of an item for specific purposes or the granting of certain rights to a person. In project management, approval is the permission to carry out subsequent work of a specified content. A release is often associated with quality control and is usually defined as a milestone in the project plan.
Actual Costs
In business cost accounting, actual costs are the costs actually incurred in a previous accounting period. In project management, actual costs are the total costs actually incurred in a project, subproject, or work package on a particular key date. Together with planned costs and progress, actual costs are important key figures for controlling (budget control, earned value analysis, etc.).
Calculation
In accounting, costing is the process of determining unit costs (of a good, service, or semifinished product), calculating the production costs of a good, and determining sales prices. A distinction can be made between preliminary costing in the planning phase and final costing after all production or trading and sales transactions have been completed. The variances from preliminary and final costing should be interpreted and fed back into cost controlling and pricing in a feedback loop.
Kapazitätsbedarf (= Ressourcenbedarf)
Unter Kapazitäts- oder Ressourcenbedarf versteht man den Bedarf an Personal und Ressourcen, die für die Abarbeitung der Arbeitspakete eines Projektes nötig sind, ermittelt aus dem geschätzten Aufwand und der Zeitrechnung des Netzplans.
Kapazitätsplanung
Die Kapazitätsplanung ist die quantitative Zuordnung der ausführenden Kapazitäten zu jedem einzelnen für das Projekt notwendigen Arbeitspaket, unter Berücksichtigung der Aufwandsschätzung. In Projectile werden die Kapazitäten als gewichteter Quotient aus der geplanten Arbeitszeit und der geplanten Projektzeit im konstanten Zeitintervall bestimmt. Das System berücksichtigt auf Wunsch auch die Wahrscheinlichkeit, dass aus dem geplanten Projekt ein Auftrag wird und gewichtet hier diese Soll-Projektzeiten entsprechend.
Kennzahlen
Kennzahlen sind konsolidierte Werte, die sich mittels Algorithmen aus Dokumentdaten oder anderen Kennzahlen berechnen lassen und die ein Dokument beschreiben. Jeder Kennzahl wird hierbei zur eindeutigen Identifikation eine ID zugeordnet. Projectile unterstützt Kennzahlen für die Masken Kontakt, Projekt, Arbeitspaket und Mitarbeiter. Die Verwendung von Kennzahlen in Projectile erlaubt es dem Anwender, Gesamtwerte, Werte zu beliebigen Zeitpunkten sowie Werte für beliebige Perioden zu erstellen. Die durch eine Kennzahl erzeugten Werte werden mit einem Erzeugungsdatum versehen, so dass sie aufbewahrt und wiederverwendet werden können, ohne dass eine erneute Berechnung nötig ist. Ferner kann jede Kennzahl einem Dokument zugeordnet werden, über die Kennzahlen in Bildschirmansichten und Reports integriert werden können.
Kostenfindung
In Projectile wird die Kostenfindung, also die Bestimmung der internen Arbeitskosten für ein Projekt, zweistufig abgebildet. Die höchste Priorität bei der Kostenfindung haben die internen Verrechnungssätze der Mitarbeiter (siehe Mitarbeiter). Diese Kosten repräsentieren die wahren Arbeitskosten. Besitzt ein Mitarbeiter diesen Verrechnungssatz nicht, wird bei der Kostenfindung der allgemeine interne Tätigkeitssatz der Firma (siehe Tätigkeit) für die Weiterbelastung verwendet.
Kostenstelle
Eine Kostenstelle ist ein nach räumlichen, funktionellen oder verrechnungstechnischen Aspekten abgegrenzter Teil einer Organisation, in dem Kosten anfallen (Verursachungsprinzip). Die Kostenstelle hat dabei die Aufgabe, die in dem definierten Bereich angefallenen Kosten zu sammeln und somit der verantwortlichen Person eine Kostenkontrolle zu ermöglichen. Weiterhin ist die Kostenstelle in den Verfahren der Vollkostenrechnung eine Voraussetzung für die Bildung von Verrechnungsätzen, die für die Kostenträgerrechnung für die Verrechnung von Gemeinkosten benötigt werden.
Kostenträger
Ein Kostenträger ist ein Bezugsobjekt, dem in der betriebswirtschaftlichen Kostenrechnung Kosten zugerechnet werden. Dabei wird in Gemeinkostenträger und absatzorientierten Kostenträger unterschieden. Die Gemeinkostenträger sind Kostenträger, welche die Kosten von innerbetrieblichen Leistungen oder Projekten sammeln, ohne dass diese jedoch zum Absatz von diesen Leistungen am Markt und damit umsatzwirksamen Erlösen führen. Die absatzorientierten Kostenträger sind Kostenträger, denen neben den leistungsbezogenen Kosten auch die erzielten Erlöse aus Umsatz zugeordnet werden. Hier entspricht der Kostenträger zugleich einem Erlösträger.
Kritischer Pfad
Der kritische Pfad kennzeichnet den Weg durch einen Netzplan, auf dem die Pufferzeiten Null sind, d.h. jede Terminüberschreitung von Aktivitäten oder Ereignissen auf dem kritischen Pfad, schlägt direkt auf den Projektendtermin durch. Alle Arbeitspakete eines Netzplans, die zeitlich nicht verschoben werden können, ohne dass sich eine Verschiebung des Projektendtermins ergibt, liegen auf dem kritischen Pfad.
Meilenstein
Ein Meilenstein ist ein signifikantes Kontrollereignis im Projektplan, definiert durch einen Termin und Ergebnisse, die zu diesem Termin in der laut Projektauftrag vereinbarten Qualität vorliegen müssen. Typische Meilensteine sind typischerweise kritische Zwischenergebnisse, Abnahmen, Produktivstarts u.ä. In Projectile werden die Meilensteine im Dokumenttyp Meilenstein definiert und die Trendtermine für die Meilenstein-Trend-Analyse im Dokumenttyp Trendtermin verwaltet.
Meilenstein-Trend-Analyse
Die Meilenstein-Trend-Analyse ist ein zukunftsbezogenes Instrument für die Terminkontrolle eines Projektes: An regelmäßigen Berichtszeitpunkten wird die Terminplanung des Projektes durch die Abfrage von Trenddaten der voraussichtlichen Meilensteinerreichung neu geschätzt. Aus dem Kurvenverlauf lässt sich ein Trend über die Termintreue des Projektes ableiten. Die Trendtermine für die Meilensteine können im Dokumenttyp Trendtermin verwaltet werden und die Analyse wird in der Projektauswertung visualisiert.
Multiprojektmanagement (=Programmmanagement)
Multiprojektmanagement ist die gleichzeitige Planung, übergreifende Steuerung und Überwachung mehrerer (untereinander abhängiger) Projekte. Hierbei werden ganze Projektportfolios betrachtet. Multiprojektmanagement bewegt sich im Spannungsfeld zwischen operativen und strategischen Entscheidungen. Dabei gilt es auf der strategischen Ebene das Projektportfolio “richtig” zusammenzustellen und die “richtigen” Schwerpunkte zu setzen, sowie auf der operativen Ebene die einzelnen Projekte wirtschaftlich abzuwickeln, Ressourcenkonflikte zu lösen und zeitlich bedingte Engpässe zu lösen.
Nachfolger
Der Nachfolger ist ein Bestandteil der Anordnungsbeziehung und bezeichnet die Zusammenhänge von Prozessen innerhalb einer Prozesskette. Bedingt durch die Logik von Bearbeitungsschritten zur Fertigung eines Produktes oder einer Dienstleistung können bestimmte Vorgänge möglicherweise erst ausgeführt werden, nachdem ein oder mehrere andere Vorgänge vollendet sind. Innerhalb der Netzplantechnik im Rahmen der Projektplanung ist der Nachfolger ein Vorgang, der einem anderen Vorgang folgt.
Netzplan
Der Netzplan ist ein Strukturmodell zur Analyse und Darstellung der logischen und zeitlichen Ablaufbedingungen eines Projektes. Ein Netzplan stellt die Vorgänge und Anordnungsbeziehungen dar und ist ein wesentliches Instrument der Projektsteuerung; speziell für die Terminplanung und -überwachung.
Netzplantechnik
Unter der Netzplantechnik versteht man ein Instrument zur Planung, Steuerung und Kontrolle von Projekten. Grundsätzlich sind dabei die Strukturplanung und Zeitplanung erforderlich; im Optimalfall gehen auch Kostenplanung und Kapazitätsplanung ein. Zwei Methoden der Netzplantechnik sind in der Praxis gebräuchlich: die Critical Path Methode (CPM) und die Metra-Potential-Methode (MPM). Bei CPM werden die Vorgänge als Pfeile dargestellt und die Knoten stellen Ereignisse dar. In vielen Fällen werden sogenannte Scheinvorgänge benötigt. Bei MPM sind die Vorgänge als Knoten dargestellt, die Pfeile zeigen die Abhängigkeiten der Knoten untereinander auf.
Organisationseinheit
Eine Organisationseinheit ist ein Element der Aufbauorganisation, die in der Regel im Organigramm visualisiert wird. Beispiele für Organisationseinheiten sind Tochterunternehmen, Niederlassungen, Bereiche oder Abteilungen. In Projectile werden Organisationseinheit mit Hilfe der Maske Unit abgebildet.
Phase
Eine Phase bezeichnet einen zeitlichen oder logischen Gliederungsabschnitt eines Projektes. Mindestens jedes Phasenende ist auch ein Meilenstein, d.h. es liegen vorgeschriebene Phasenergebnisse vor. Die Gliederung von Projekten in bestimmte Phasen wird Phasenmodell genannt.
Portfolio (=Projektportfolio)
In der Betriebswirtschaft versteht man unter Portfolio eine Zusammenstellung von Investitionen. Dem Aufbau eines Portfolios geht in der Regel eine umfangreiche Analyse voraus. Der Besitz eines Portfolios ist in der Regel Teil einer Strategie, die Risiken finanzieller Investitionen durch Streuung zu senken. Das Portfolio eines Unternehmens beschreibt die Geschäftsfelder, das Produktportfolio ist die weitere Verfeinerung des Unternehmensportfolios bis zum einzelnen Produkt und das Projektportfolio ist die Menge oder eine Teilmenge aller laufenden Projekte einer Organisation.
Portfolio-Management (=Projektportfolio-Management)
Unter Portfoliomanagement versteht man die Verwaltung eines Portfolios, d.h. eines Bestandes an Investitionen. Der Portfoliomanagementprozess beinhaltet die Portfolioplanung (Selektion und Analyse), die Portfoliorealisation (Monitoring und Revision) sowie die Portfoliokontrolle (Performancemessung, Attribution). Im Bezug auf Projekte stehen Fragen nach der Ausrichtung der Projektziele an der Unternehmensstrategie, der Projektbewertung und die Ertragsaussichten von Projekten im Vordergrund. Zu den Methoden des Portfoliomanagements gehören die Zusammenstellung, Strukturierung und Kennzahlenbestimmung von Portfolios, die Bewertung und Priorisierung der Investitionen sowie die Simulation möglicher Portfolios.
Preisfindung
Hierarchie für die externe Preisfindung:
| Dokument | Feld | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arbeitspaket | Externer Stundensatz |
| 2 | Projekt | Externer Stundensatz |
| 3 | Oberprojekt | Externer Stundensatz (rekursiv hinauf die Projekthierarchie) |
| 4 | Kontakt | Externer Stundensatz |
| 5 | Projektweise Tätigkeit | Externer Stundensatz (rekursiv hinauf die Projekthierarchie) |
| 6 | Kundenweise Tätigkeit | Externer Stundensatz |
| 7 | Projektweiser Mitarbeitersatz | Externer Stundensatz (rekursiv hinauf die Projekthierarchie) |
| 8 | Kundenweiser Mitarbeitersatz | Externer Stundensatz |
| 9 | Tätigkeit | Externer Stundensatz |
Verwendung von externen Stundensätzen im Mitarbeiter bzw. Mitarbeitervertrag:
Wenn externe Stundensätze pro Mitarbeiter oder Mitarbeitervertrag verwendet werden, dann muss man in der Projectile Default das Flag “Externer Stundensatz Mitarbeiter” setzen.
Wenn es gesetzt ist und die Felder Externer Stundensatz oder Externe Stundensätze im Mitarbeiter oder Mitarbeitervertrag gefüllt sind, dann hat dieser die höchste Priorität.
Wenn die Mitarbeitersätze als letztes berücksichtigt werden sollen, dann muss in der Projectile Default das Flag “Externe Mitarbeitersätze mit letzter Priorität” aktiviert werden.
| Dokument | Feld | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mitarbeiter | Externe Stundensätze (Datumsbehafteter Satz im Mitarbeiter) |
| 2 | Mitarbeitervertrag | Externer Stundensatz (Datumsbehafteter Satz im MA-Vertrag) |
| 3 | Arbeitspaket | Externe Stundensätze (Datumsbehafteter Satz im Arbeitspaket) |
| 4 | Arbeitspaket | Externer Stundensatz |
| 5 | Projekt | Externe Stundensätze (Datumsbehafteter Satz im Projekt) |
| 6 | Mitarbeiter | Externer Stundensatz |
Wenn kein datumsbehafteter Satz ermittelt werden kann, gilt die zuerst genannte Hierarchie.
Profit
Profit ist der auf dem Markt realisierte, in Geld oder Prozent ausgedrückte Mehrwert, der Ziel des marktwirtschaftlichen Produktionsprozesses ist. Umgangssprachlich wird der Profit als Synonym für Gewinn gebraucht. In Projectile wird der Profit eines Projektes als Differenz von Umsatz und Kosten bestimmt, also Profit [EUR] = Umsatz [EUR] - Kosten [EUR]. Der prozentuale Profit wird bestimmt als Quotient aus absoluten Profit durch Umsatz: Profit [%] = (Profit [EUR] / Umsatz [EUR]) * 100.
Projekt
Ein Projekt ist ein Vorhaben, das im wesentlichen durch Einmaligkeit der Bedingungen in ihrer Gesamtheit gekennzeichnet ist und folgende Kriterien erfüllt:
- Einmaligkeit, keine Routinetätigkeit
- eindeutige Zielvorgabe
- zeitliche, finanzielle, personelle oder andere Begrenzungen
- hohe Komplexität (Indikatoren: Aufwand, Anzahl an beteiligten Abteilungen, Risiko)
Die Projekte in Projectile werden im Dokumenttyp Projekt verwaltet.
Projektcontrolling
Projektcontrolling ist eine Methode zum frühzeitigen Erkennen von Projektabweichungen mit Hilfe von Vergleichen der Plan- und Ist-Ergebnisse. Zur Beurteilung der Abweichungen wird der Projektbericht oder eine Auswertung des Projektleiters herangezogen. Die Vorgehensweise für das Projektcontrolling muß im Projektauftrag bereits festgelegt sein. In Projectile werden Auswertungen für das Controlling (Soll/Ist-Vergleiche für Projekte, Arbeitspakete und Zeiten) in der Projektauswertung generiert.
Projektdokumentation
Die Projektdokumentation ist (nach DIN 69901) die Zusammenstellung ausgewählter, wesentlicher Daten über Konfiguration, Organisation, Mitteleinsatz, Lösungswege, Ablauf und erreichte Ziele des Projektes. Eine Projektdokumentation besteht mindestens aus Projektberichten, Projektabschlussberichten und Pflichtenheft bzw. Spezifikationen.
Projektkoordination
Die Projektkoordination ist die zentrale Form der Projektrahmenorganisation. Für die Dauer eines Projektes wird die bestehende Linienorganisation um die Stabsfunktion eines Projektkoordinators erweitert. Sie besitzt in der Regel aber keine Entscheidungs- und Weisungsbefugnis gegenüber den Linienfunktionen.
Projektleiter
Ein Projektleiter ist der Verantwortliche für die Erreichung der im Projektauftrag definierten Projektziele. Er ist der zentrale Ansprechpartner des Auftraggebers. Aufgaben, Befugnisse und Verantwortung des Projektleiters sollten unternehmensweit festgelegt sein. In Projectile wird der Projektleiter (und gegebenenfalls sein Stellvertreter) im Dokumenttyp Projekt definiert.
Projektmanagement
Projektmanagement ist eine Konzeption, die dazu dient, Projekte zielorientiert und effizient abzuwickeln. Dazu gehören organisatorische, methodische und zwischenmenschliche Aspekte (siehe auch Abschnitt 1).
Projektmitarbeiter
Projektmitarbeiter sind prinzipiell alle an einem Projekt beteiligten Personen, auch wenn sie nicht direkt zum Projektteam gehören. Die Projektmitarbeiter in Projectile werden im Dokumenttyp Mitarbeiter verwaltet.
Projektplan
Der Projektplan besteht aus diversen Teilplänen zur Durchführung eines Projektes und werden vom Projektleiter oder Projektteam erstellt. Dieser Plan beinhaltet Organisationsplan, Terminplan, Budgetplan, Personalplan, Aktivitätenplan, Einführungsplan, Risikoplan und Qualitätsplan. Je nach Projektart können spezifische Pläne hinzukommen wie Migrations- oder Testplan.
Project Planning
Project planning includes all activities that lead to a project plan. A project plan can consist of the following elements:
- work breakdown structure with work package descriptions
- Schedule (network, bar chart, milestone plan)
- Resource plan
- Cost plan
- Risk analysis
Project Risk (= Risk)
A risk is the calculated forecast of a possible damage or loss in the negative case or a possible benefit or profit in the positive case (opportunity). What is perceived as damage or benefit depends on values. A risk is the probability of the occurrence of a negative event (mathematical) or the probability of the occurrence of a negative event multiplied by the financial extent (business administration). A project risk can be qualified in terms of its probability of occurrence, its effects (delay, cost increase, loss of quality) and the damage it causes.
Project Structuring
Project structuring is the development of a work breakdown structure. A project is divided hierarchically into smaller and smaller elements from project, through the sub-projects to the work packages. The lowest level of structuring is the basis for the further project planning.
Work Breakdown Structure
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is the division of a project into work-related parts, such as phases, work orders, and work steps.
In Projectile, work breakdown structures are generated in the project evaluation.
Project Team
The project team consists of the project staff who, together with the project leader, are responsible for project implementation. The project team is defined in the project document type for each parent project.
Project Goal
The project goal is part of project order and consists of three components
- Content
- Time
- Costs
It must be accessible, complete, consistent, testable, documented and agreed between client and project management.
Buffer Time
The buffer time is a term from the network planning technique. The buffer time is a time frame for the execution of an activity. This leeway can be used by shifting the activity and/or by extending the activity duration. You can determine four types of float time in a network by entering several specifications. The total float and the free float are the most commonly used. The total float GPi of activity i is calculated from the difference between SAZi (latest start time of i) and FAZi (earliest start time of i), or SEZi (latest finish time of i) and FEZi (earliest finish time of i). This means that the total float indicates by how much the activity can be shifted without jeopardizing the end of the project: GPi = SAZi - FAZi = SEZi - FEZi. The Free Buffer is the time that does not endanger the earliest possible start or end of the successor. (Formally: all successor operations can be performed in their earliest position). It can only occur if at least two completed operations meet the same successor. It is calculated for a “normal sequence” (end - start) by forming the difference between the earliest end of the activity in question and the earliest start of its successor. In the case of a start sequence (start - start) the earliest start dates of the operations are compared and in the case of a finish sequence (finish - finish) the earliest finish dates of the operations are compared. Beyond that.
Invoicing (= Settlement of Expenses)
In the case of invoicing, goods or services provided by the supplier are remunerated by the buyer according to agreement. Remuneration can be based on expenses or fixed prices and is usually controlled by payment plans. In the case of an effort-based remuneration, the customer often requests a detailed list of all expenses or costs incurred when issuing the invoice. DIN 69903 interprets invoicing as the entire process from cost recording, allocation and invoicing to the recognition of the invoice. In Projectile this functionality is represented by the invoicing module.
Resources
Resources are personnel and material resources that are required for the execution of activities, work packages or projects (DIN 69902). The unit of measurement for resources can be either a unit of value (Euro, US Dollar…) or a unit of quantity (working hours, machine running times, tons of building material, etc.). You assign resources to a project by specifying times and periods when they are available to the project.
Resource Management
The disposition of personnel, material resources and other aids required for project work is the task of resource management. The aim of resource management is to ensure that resources are used optimally and that projects are supplied with these resources as fairly as possible. The operating times for resources must be kept as short as possible, since they burden the project budget with the corresponding costs. From the point of view of the organization, the aim is to achieve the most even and high utilization of resources.
Backward Calculation (= Backward Scheduling)
Within the network planning technique, forward and backward calculations are required to determine the total project duration, earliest and latest dates and buffer times. Backward calculation is the method of planning a project from its scheduled end. In scheduling, a deadline is specified by which the project result must be completed. Scheduling is then carried out from the end date backwards to the latest possible start date of the project.
SPI
The SPI (Schedule Performance Index) is the time-related performance indicator used in earned value analysis. It is formed from the ratio of earned value and plan expenses. This means that if the SPI is greater than 1.00 (100%), the project results have been achieved faster than originally planned, whereas if the SPI is less than 1.00 (100%), the project is progressing too slowly.
Subproject
In practice, larger projects are broken down into sub-projects according to certain criteria (functional, organisational, technical, etc.) in order to be better managed and administered. When subprojects are divided up over time, they are often referred to as project phases.
Scheduling
Scheduling includes the planning of the start and end times of all work packages of a project.
TopDown Planning
Top-down planning refers to project planning according to the top-down principle. Here, activities, processes, times, and costs are planned in detail at project level, and this planning results in restrictions for the lower levels (subprojects and work packages).
TopDown Principle
In project management, the top-down principle refers to the general procedure for processing or planning from the superordinate projects to the individual work packages (i.e. from top to bottom: overall project - subprojects - work package).
Process
The work packages that are defined in work breakdown structure planning are activities (in the sense of network planning). The activities are then linked to each other by relationships. Depending on the network type, activities are symbolized by arrows or nodes. During project planning, activities are formed from the work packages.
Predecessor
The predecessor is a component of the relationship and describes the relationships between processes within a process chain. Due to the logic of processing steps for the production of a product or service, certain operations may only be executed after one or more other operations have been completed. In network technology in project planning, the predecessor is an activity that precedes another activity.
Forward Calculation (= Forward Scheduling)
Within the network planning technique, forward and backward calculations are required to determine the total project duration, earliest and latest dates and buffer times. Forward calculation determines the end time starting from the start of the project. In accordance with the relationships, all activities and events are entered one after the other from the start of the process with their respective durations, time intervals, floats, and so on, in the appropriate calendar.
Knowledge Management
Knowledge management describes a direction of management theory that aims to use and develop knowledge in organizations in order to achieve the company goals in the best possible way. Contributions to knowledge management are developed in many disciplines, especially in business informatics, business administration, computer science, social science or information science.
Payment Plan
A payment plan denotes a sequence of invoices where the total price is paid in a series of instalments according to the previously agreed dependency of delivery and instalments.